Description
In general, given the preorder traversal sequence and postorder traversal sequence of a binary tree, we cannot determine the binary tree.
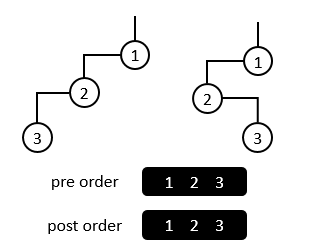
Figure 1
In Figure 1 for example, although they are two different binary tree, their preorder traversal sequence and postorder traversal sequence are both of the same.
But for one proper binary tree, in which each internal node has two sons, we can uniquely determine it through its given preorder traversal sequence and postorder traversal sequence.
Label n nodes in one binary tree using the integers in [1, n], we would like to output the inorder traversal sequence of a binary tree through its preorder and postorder traversal sequence.
Input
The 1st line is an integer n, i.e., the number of nodes in one given binary tree,
The 2nd and 3rd lines are the given preorder and postorder traversal sequence respectively.
Output
The inorder traversal sequence of the given binary tree in one line.
Example
Input
5
1 2 4 5 3
4 5 2 3 1
Output
4 2 5 1 3
Restrictions
For 95% of the estimation, 1 <= n <= 1,000,00
For 100% of the estimation, 1 <= n <= 4,000,000
The input sequence is a permutation of {1,2…n}, corresponding to a legal binary tree.
Time: 2 sec
Memory: 256 MB
Hints
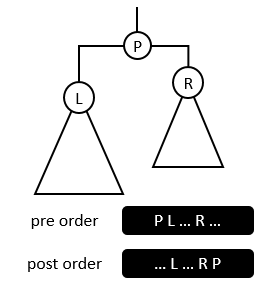
Figure 2
In Figure 2, observe the positions of the left and right children in preorder and postorder traversal sequence.
描述
一般来说,给定二叉树的先序遍历序列和后序遍历序列,并不能确定唯一确定该二叉树。

(图一)
比如图一中的两棵二叉树,虽然它们是不同二叉树,但是它们的先序、后序遍历序列都是相同的。
但是对于“真二叉树”(每个内部节点都有两个孩子的二叉树),给定它的先序、后序遍历序列足以完全确定它的结构。
将二叉树的n个节点用[1, n]内的整数进行编号,输入一棵真二叉树的先序、后序遍历序列,请输出它的中序遍历序列。
输入
第一行为一个整数n,即二叉树中节点的个数。
第二、三行为已知的先序、后序遍历序列。
限制
对于95%的测例:1 ≤ n ≤ 1,000,000
对于100%的测例:1 ≤ n ≤ 4,000,000
输入的序列是{1,2…n}的排列,且对应于一棵合法的真二叉树
时间:2 sec
空间:256 MB
提示

观察左、右孩子在先序、后序遍历序列中的位置
重温视频05e5-3
 Background
Background