Description
Figure 1 shows the structure of a station for train dispatching.
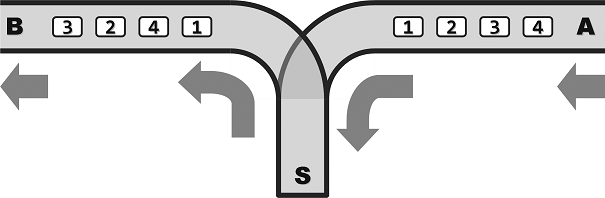
Figure 1
In this station, A is the entrance for each train and B is the exit. S is the transfer end. All single tracks are one-way, which means that the train can enter the station from A to S, and pull out from S to B. Note that the overtaking is not allowed. Because the compartments can reside in S, the order that they pull out at B may differ from that they enter at A. However, because of the limited capacity of S, no more that m compartments can reside at S simultaneously.
Assume that a train consist of n compartments labeled {1, 2, …, n}. A dispatcher wants to know whether these compartments can pull out at B in the order of {a1, a2, …, an} (a sequence). If can, in what order he should operate it?
Input
Two lines:
1st line: two integers n and m;
2nd line: n integers separated by spaces, which is a permutation of {1, 2, …, n}. This is a compartment sequence that is to be judged regarding the feasibility.
Output
If the sequence is feasible, output the sequence. “Push” means one compartment goes from A to S, while “pop” means one compartment goes from S to B. Each operation takes up one line.
If the sequence is infeasible, output a “no”.
Example 1
Input
5 2
1 2 3 5 4
Output
push
pop
push
pop
push
pop
push
push
pop
pop
Example 2
Input
5 5
3 1 2 4 5
Output
No
Restrictions
1 <= n <= 1,600,000
0 <= m <= 1,600,000
Time: 2 sec
Memory: 256 MB
描述
某列车调度站的铁道联接结构如Figure 1所示。
其中,A为入口,B为出口,S为中转盲端。所有铁道均为单轨单向式:列车行驶的方向只能是从A到S,再从S到B;另外,不允许超车。因为车厢可在S中驻留,所以它们从B端驶出的次序,可能与从A端驶入的次序不同。不过S的容量有限,同时驻留的车厢不得超过m节。
设某列车由编号依次为{1, 2, …, n}的n节车厢组成。调度员希望知道,按照以上交通规则,这些车厢能否以{a1, a2, …, an}的次序,重新排列后从B端驶出。如果可行,应该以怎样
的次序操作?
输入
共两行。
第一行为两个整数n,m。
第二行为以空格分隔的n个整数,保证为{1, 2, …, n}的一个排列,表示待判断可行性的驶出序列{a1,a2,…,an}。
输出
若驶出序列可行,则输出操作序列,其中push表示车厢从A进入S,pop表示车厢从S进入B,每个操作占一行。
若不可行,则输出No。
样例
见英文题面
限制
1 ≤ n ≤ 1,600,000
0 ≤ m ≤ 1,600,000
时间:2 sec
空间:256 MB
模拟栈混洗:(自写Stack,因为该OJ禁止STL)
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 | #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> template <typename T> struct Stack{ private: int _capacity; int _size; T * array; public: Stack(int capacity){ this->array=new T[capacity]; this->_capacity=capacity; this->_size=0; } ~Stack(){ delete [] array; } bool empty(){ return (_size==0); } bool full(){ return (_size==_capacity); } int size(){ return _size; } void push(T content){ this->array[_size]=content; _size++; } void pop(){ _size--; } T & top(){ return array[_size-1]; } }; int main(){ int n,m; scanf("%d %d",&n,&m); Stack<int> S(m); bool * record=new bool[2*n+1]; int * array=new int[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++)scanf("%d",array+i); int arrptr=0,recordptr=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(!S.full()){ S.push(i); record[recordptr++]=true; while(!S.empty()&&array[arrptr]==S.top()){ S.pop(); record[recordptr++]=false; arrptr++; } }else{ printf("No"); return 0; } } if(!S.empty()){ printf("No"); return 0; }else{ for(int i=0;i<recordptr;i++){ if(record[i])printf("push\n"); else printf("pop\n"); } return 0; } } |