下面我来写一下自己个人的题解:
本人博客链接:https://renjikai.com/ustc-hack-ctf-8-writeup/
签到
直接改GET的参数Page定位到要求的页面就行了。
进制十六——参上
光把ASCII字符打码,十六进制Hex没打码没任何意义啊!!手动输进WinHex里或者010Editor里就完事了。
去吧!追寻自由的电波
这题我还想了半天怎么搞,最后发现把音频播放速度降速到20%就行,听播放的每个单词的首字母,拼起来即可。
猫咪问答 Pro Max
搜索引擎搜搜搜。
卖瓜
利用PHP的整型溢出,先溢出成负数,在加回到正数即可。
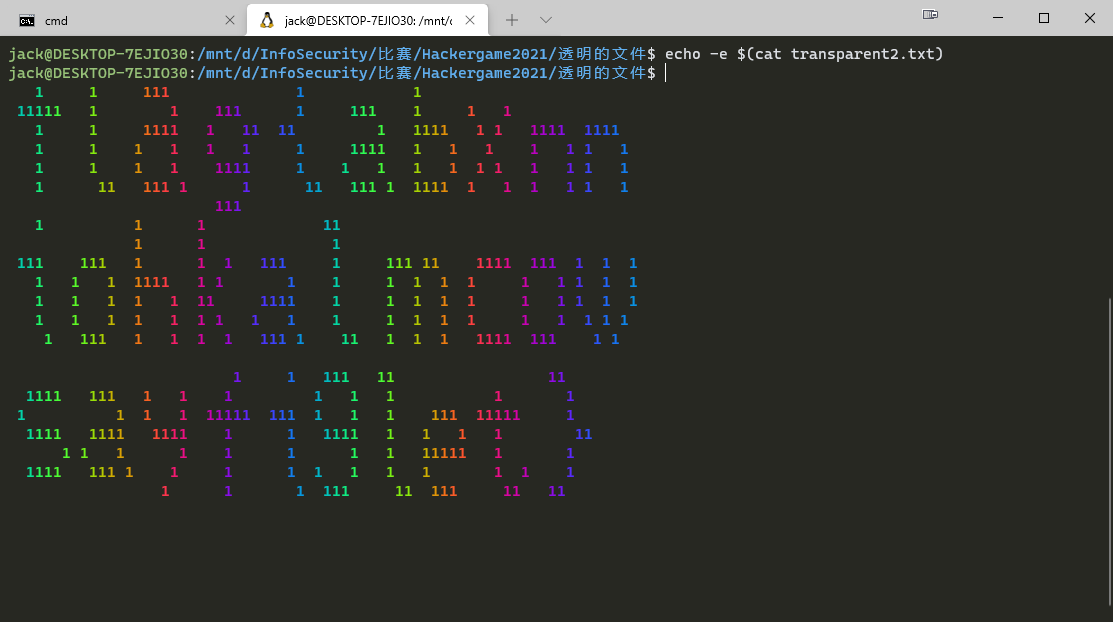
透明的文件
原文件的格式一看,好像之前在Linux终端里面转义,显示带颜色的字符时用过。遂查找了一下,发现转义的字符前面都需要带\033[,所以这个源文件的格式里面全都差了\033,把它补齐。
然后在Linux终端里使用echo -e打印,发现打印出来在满是字符的背景上抠出了一些空白。于是猜想,要把里面的空格换成任意字符才能看的出来,于是我就把空格全部替换为1。
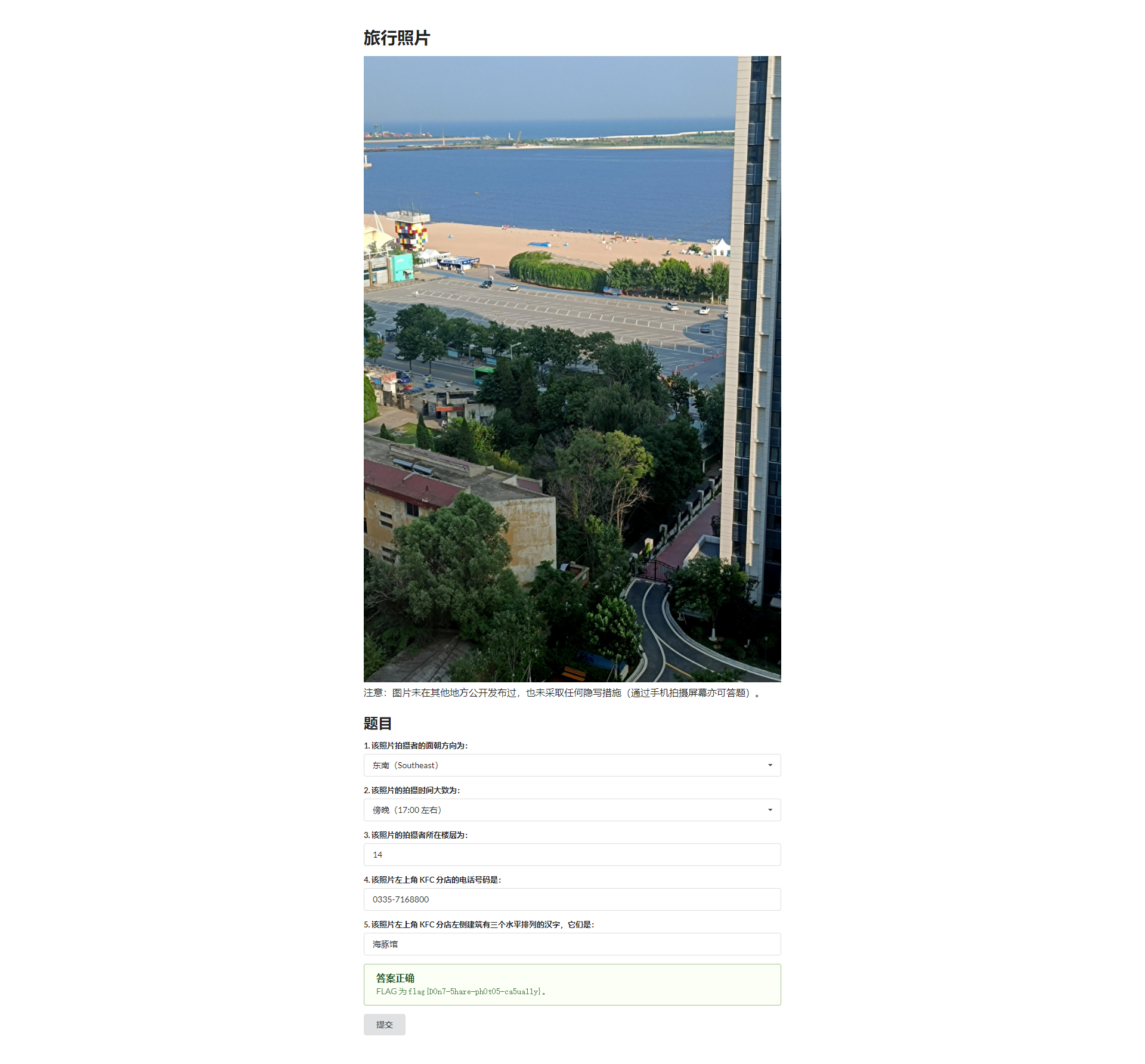
旅行照片
通过蓝色的肯德基定位到秦皇岛国内唯一蒂芙尼蓝色肯德基,然后百度地图疯狂查询再加上一通暴力瞎试可以得出答案。
FLAG 助力大红包
活动规则里写了个使用前后端方式检查用户IP,前端检查就是form里面用javascript拿了个IP,后端就是从PHP里面读,但是从PHP里读,可以在HTTP包头里加个X-Forwarded-For绕过,也挺简单的。还要求的是不同/8的IP地址,那就从0.0.0.0/8一直到255.0.0.0/8挨个的Submit过去就完了。
图之上的信息
使用GraphQL的内省查询,把它的内部结构全都导出来,然后按照他支持的查询方式查询就行了。
可以参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/390876937
Easy RSA
原脚本:
import math
import sympy
from Crypto.Util.number import *
e = 65537
def get_p(): #威尔逊定理
x = 11124440021748127159092076861405454814981575144744508857178576572929321435002942998531420985771090167262256877805902135304112271641074498386662361391760451
y = 11124440021748127159092076861405454814981575144744508857178576572929321435002942998531420985771090167262256877805902135304112271641074498386662361391661439
value_p = sympy.nextprime((math.factorial(y)) % x) # Hint:这里直接计算会溢出,请你仔细观察 x 和 y 的特征
return value_p
def get_q():
value = [getPrime(256)]
for i in range(1, 10):
value.append(sympy.nextprime(value[i - 1]))
print("value[-1] = ", value[-1])
# value[-1] = 80096058210213458444437404275177554701604739094679033012396452382975889905967
n = 1
for i in range(10):
n = n * value[i]
q = getPrime(512)
value_q = pow(q, e, n) #多素数RSA系统
print("value_q = ", value_q)
# value_q = 5591130088089053683141520294620171646179623062803708281023766040254675625012293743465254007970358536660934858789388093688621793201658889399155357407224541324547522479617669812322262372851929223461622559971534394847970366311206823328200747893961649255426063204482192349202005330622561575868946656570678176047822163692259375233925446556338917358118222905050574458037965803154233167594946713038301249145097770337253930655681648299249481985768272321820718607757023350742647019762122572886601905212830744868048802864679734428398229280780215896045509020793530842541217790352661324630048261329493088812057300480085895399922301827190211956061083460036781018660201163819104150988531352228650991733072010425499238731811243310625701946882701082178190402011133439065106720309788819
return sympy.nextprime(q)
# this destroyes the rsa cryptosystem
p = get_p()
q = get_q()
m = int.from_bytes(open("flag.txt", "rb").read(), "big")
c = pow(m, e, p * q)
print("c = ", c)
# c = 110644875422336073350488613774418819991169603750711465190260581119043921549811353108399064284589038384540018965816137286856268590507418636799746759551009749004176545414118128330198437101472882906564195341277423007542422286760940374859966152871273887950174522820162832774361714668826122465471705166574184367478
搜索一下可以发现用到了数论中的威尔逊定理和多素数RSA系统,写个脚本解密即可。
答案如下:
import gmpy2, sympy
e = 65537
def get_p(): #https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45859850/article/details/111462791
# x, y is prime
x = 11124440021748127159092076861405454814981575144744508857178576572929321435002942998531420985771090167262256877805902135304112271641074498386662361391760451
y = 11124440021748127159092076861405454814981575144744508857178576572929321435002942998531420985771090167262256877805902135304112271641074498386662361391661439
# (x-1)! % x = -1 % x
result = gmpy2.powmod(-1, 1, x)
for i in range(y+1, x):
result = (gmpy2.invert(i, x) * result) % x
return sympy.nextprime(result)
def get_q():
value = [80096058210213458444437404275177554701604739094679033012396452382975889905967]
for i in range(9):
value.append(sympy.prevprime(value[i]))
phi = 1
n = 1
for i in range(len(value)):
phi *= value[i] - 1
n *= value[i]
d = gmpy2.invert(e, phi)
c = 5591130088089053683141520294620171646179623062803708281023766040254675625012293743465254007970358536660934858789388093688621793201658889399155357407224541324547522479617669812322262372851929223461622559971534394847970366311206823328200747893961649255426063204482192349202005330622561575868946656570678176047822163692259375233925446556338917358118222905050574458037965803154233167594946713038301249145097770337253930655681648299249481985768272321820718607757023350742647019762122572886601905212830744868048802864679734428398229280780215896045509020793530842541217790352661324630048261329493088812057300480085895399922301827190211956061083460036781018660201163819104150988531352228650991733072010425499238731811243310625701946882701082178190402011133439065106720309788819
m = pow(c, d, n)
return sympy.nextprime(m)
p = get_p()
print(p)
q = get_q()
print(q)
n = p * q
phi = (p-1)*(q-1)
d = gmpy2.invert(e, phi)
c = 110644875422336073350488613774418819991169603750711465190260581119043921549811353108399064284589038384540018965816137286856268590507418636799746759551009749004176545414118128330198437101472882906564195341277423007542422286760940374859966152871273887950174522820162832774361714668826122465471705166574184367478
m = pow(c, d, n)
print((int(m)).to_bytes(200, "big"))
Amnesia
哈哈,终于来到重头戏了!前面都是比较简单的题目,没有啥可说的,干就完了。这道题目才是比较好玩的!不枉我把《程序员的自我修养》全看了一遍,在这里全都用上了,哈哈!
官方题解里夸得应该就是我吧,哈哈。下面我来讲一下我做这道题目的思路。
轻度失忆
编译后 ELF 文件的 .data 和 .rodata 段会被清零。
对于轻度失忆,我们需要保证存储的字符串不在.data和.rodata这两个静态数据段,这要求我们开的变量不能是匿名的,例如,不能直接用puts("Hello, world!");。因为匿名的数据肯定就存在了.rodata段。像官方题解那样一个一个putchar也没问题,但是就是有点麻烦。所以有什么好办法呢?
答案如下:
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
char buf[] = "Hello, world!";
printf(buf);
}
为什么这道题能行得通呢?通过代码可以看出,缓冲区buf是一个自动变量,而对于自动变量,编译器会将其开在栈上。而对于栈变量的初始化,当初始化值的size较小时,编译器会将对其的初始化值硬编码到代码段中。例如,上面这段代码的Intel汇编为:
main:
lea ecx, [esp+4]
and esp, -16
push DWORD PTR [ecx-4]
push ebp
mov ebp, esp
push ecx
sub esp, 32
mov DWORD PTR [ebp-22], 1819043144
mov DWORD PTR [ebp-18], 1998597231
mov DWORD PTR [ebp-14], 1684828783
mov WORD PTR [ebp-10], 33
lea eax, [ebp-22]
push eax
call printf
add esp, 16
mov eax, 0
mov ecx, DWORD PTR [ebp-4]
leave
lea esp, [ecx-4]
ret
直接把初始化内容硬编码进了代码段。
当自动变量的size超过某个limit后,如果还采用将初始化值硬编码到代码段的方法,会造成指令序列过长。因此,编译器就会继续自动把初始化值放到.rodata段。
例如,下面这个代码,可以看出缓冲区内要存储的字符数很多:
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
char buf[] = "Hellabrgvwejgvbwejkvgbwejbgvewbgkjvnbwernbfgjkewbgjkvewrjgvbwerjkgvbwesbgvjewrsbkgjfvbwejgbvekjrgbvjkerdbscfsavdsbvewsgvbeswgvwesfgvwesgo, world!";
printf(buf);
}
编译器会将其编译为:
.LC0:
.string "Hellabrgvwejgvbwejkvgbwejbgvewbgkjvnbwernbfgjkewbgjkvewrjgvbwerjkgvbwesbgvjewrsbkgjfvbwejgbvekjrgbvjkerdbscfsavdsbvewsgvbeswgvwesfgvwesgo, world!"
main:
lea ecx, [esp+4]
and esp, -16
push DWORD PTR [ecx-4]
push ebp
mov ebp, esp
push edi
push esi
push ecx
sub esp, 184
mov eax, DWORD PTR .LC0
mov DWORD PTR [ebp-170], eax
mov eax, DWORD PTR .LC0+142
mov DWORD PTR [ebp-28], eax
lea edi, [ebp-168]
mov esi, OFFSET FLAT:.LC0+2
mov ecx, 36
rep movsd
lea eax, [ebp-170]
push eax
call printf
add esp, 16
mov eax, 0
lea esp, [ebp-12]
pop ecx
pop esi
pop edi
pop ebp
lea esp, [ecx-4]
ret
可以看出应用了串操作指令。
对于”Hello, world!” 这个长度的字符串,还在第一种情况的范围之内。因此我们无需使用官方题解里比较麻烦的方法,哈哈。
记忆清除
编译后 ELF 文件的 .text 段会被清零。
在看这道题之前,我们首先明确一下,根据这个编译选项可知,该程序是动态链接的。并且程序开启了PIE。
对于动态链接的程序,程序的入口点始终是动态链接器ld,由ld首先负责填好程序中共享对象的初始化[1],使得对外部符号的引用得以成功进行。然后ld将程序控制权移交给_start,由_start调用__libc_start_main,完成程序各静态数据段变量的构造,然后再将控制权移交给main,main执行完毕之后,再返回__libc_start_main,完成程序各静态数据段变量的析构,并通过系统调用通知操作系统要求本进程终止运行[2][3][4]。
那一看就知道,.text清零了啥都别干了,肯定得换节啊,查手册[5][6],找到了section。
section ("section-name")
Normally, the compiler places the code it generates in the text section. Sometimes, however, you need additional sections, or you need certain particular functions to appear in special sections. The section attribute specifies that a function lives in a particular section. For example, the declaration:
extern void foobar (void) __attribute__ ((section ("bar")));
puts the function foobar in the bar section.
Some file formats do not support arbitrary sections so the section attribute is not available on all platforms. If you need to map the entire contents of a module to a particular section, consider using the facilities of the linker instead.
好啊,那就换节名吧,换成什么呢,换成init吧,吉利啊。(我当时做这道题的时候,以为其他初始化函数也存在这个节里,但我刚做了个实验发现不是,是.init,加不加点是有区别的)
但是换成init节名,只是逃离了被清零的命运,不解决任何其他问题,没有在_start里注册,我于是又找啊找,找到了constructor和destructor,内容如下:
constructor
destructor
constructor (priority)
destructor (priority)
The constructor attribute causes the function to be called automatically before execution enters main (). Similarly, the destructor attribute causes the function to be called automatically after main () completes or exit () is called. Functions with these attributes are useful for initializing data that is used implicitly during the execution of the program.
On some targets the attributes also accept an integer argument to specify a priority to control the order in which constructor and destructor functions are run. A constructor with a smaller priority number runs before a constructor with a larger priority number; the opposite relationship holds for destructors. Note that priorities 0-100 are reserved. So, if you have a constructor that allocates a resource and a destructor that deallocates the same resource, both functions typically have the same priority. The priorities for constructor and destructor functions are the same as those specified for namespace-scope C++ objects (see C++ Attributes). However, at present, the order in which constructors for C++ objects with static storage duration and functions decorated with attribute constructor are invoked is unspecified. In mixed declarations, attribute init_priority can be used to impose a specific ordering.
Using the argument forms of the constructor and destructor attributes on targets where the feature is not supported is rejected with an error.
然后我就以为往function前头再加个__attribute__((constructor))就可万事大吉,但是我错了。。发现不行。。这个时候代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
__attribute__((section("init"))) __attribute__((constructor))
void init_extra(){
char buf[] = "Hello, world!";
puts(buf);
exit(0);
}
int main(){}
后来发现,_start就在.text节里,_start执行不了就调用不了libc的初始化,初始化不了,你函数带了constructor的attribute也无半毛钱用,遂无法,开始用IDA和objdump看起来汇编,gdb瞎跑。
好,神奇的事情出现了,gdb跑出了SIGSEGV,如下图:
[----------------------------------registers-----------------------------------]
EAX: 0xf7fe7950 --> 0x565e6000 --> 0x464c457f
EBX: 0xf7fe7000 --> 0x28f2c
ECX: 0x0
EDX: 0xf7fce520 (push ebp)
ESI: 0xffc6698c --> 0xffc67f26 ("HOSTNAME=e646a85ed9d7")
EDI: 0x565e7070 (<_start>: add BYTE PTR [eax],al)
EBP: 0x0
ESP: 0xffc66980 --> 0x1
EIP: 0x565e7210 (<__libc_csu_fini>: add BYTE PTR [ebx-0x7d],dl)
EFLAGS: 0x10247 (CARRY PARITY adjust ZERO sign trap INTERRUPT direction overflow)
[-------------------------------------code-------------------------------------]
0x565e720a: add BYTE PTR [eax],al
0x565e720c: add BYTE PTR [eax],al
0x565e720e: add BYTE PTR [eax],al
=> 0x565e7210 <__libc_csu_fini>: add BYTE PTR [ebx-0x7d],dl
0x565e7213 <init_extra+2>: in al,dx
0x565e7214 <init_extra+3>: and al,0xe8
0x565e7216 <init_extra+5>: xchg esi,eax
0x565e7217 <init_extra+6>: (bad)
[------------------------------------stack-------------------------------------]
0000| 0xffc66980 --> 0x1
0004| 0xffc66984 --> 0xffc67f1a ("/root/a.out")
0008| 0xffc66988 --> 0x0
0012| 0xffc6698c --> 0xffc67f26 ("HOSTNAME=e646a85ed9d7")
0016| 0xffc66990 --> 0xffc67f3c ("SHLVL=1")
0020| 0xffc66994 --> 0xffc67f44 ("HOME=/root")
0024| 0xffc66998 --> 0xffc67f4f ("OLDPWD=/")
0028| 0xffc6699c --> 0xffc67f58 ("_=/usr/bin/gdb")
[------------------------------------------------------------------------------]
Legend: code, data, rodata, value
Stopped reason: SIGSEGV
0x565e7210 in __libc_csu_fini ()
我一看,这有戏啊,IP自己从_start跑到init_extra了,遂objdump -d看一下。(后面的汇编都是AT&T汇编,有的地方可能会被代码编辑器吞掉,意会一下即可)
root@e646a85ed9d7:~# objdump -d a.out
a.out: file format elf32-i386
Disassembly of section .init:
00001000 <_init>:
1000: 53 push %ebx
1001: 83 ec 08 sub 0x8,%esp
1004: e8 a7 00 00 00 call 10b0 <__x86.get_pc_thunk.bx>
1009: 81 c3 f7 2f 00 00 add0x2ff7,%ebx
100f: 8b 83 f4 ff ff ff mov -0xc(%ebx),%eax
1015: 85 c0 test %eax,%eax
1017: 74 02 je 101b <_init+0x1b>
1019: ff d0 call *%eax
101b: 83 c4 08 add 0x8,%esp
101e: 5b pop %ebx
101f: c3 ret
Disassembly of section .plt:
00001020 <.plt>:
1020: ff b3 04 00 00 00 pushl 0x4(%ebx)
1026: ff a3 08 00 00 00 jmp *0x8(%ebx)
102c: 00 00 add %al,(%eax)
...
00001030 <puts@plt>:
1030: ff a3 0c 00 00 00 jmp *0xc(%ebx)
1036: 68 00 00 00 00 push0x0
103b: e9 e0 ff ff ff jmp 1020 <.plt>
00001040 <exit@plt>:
1040: ff a3 10 00 00 00 jmp *0x10(%ebx)
1046: 68 08 00 00 00 push 0x8
104b: e9 d0 ff ff ff jmp 1020 <.plt>
00001050 <__libc_start_main@plt>:
1050: ff a3 14 00 00 00 jmp *0x14(%ebx)
1056: 68 10 00 00 00 push0x10
105b: e9 c0 ff ff ff jmp 1020 <.plt>
Disassembly of section .plt.got:
00001060 <__cxa_finalize@plt>:
1060: ff a3 f0 ff ff ff jmp *-0x10(%ebx)
1066: 66 90 xchg %ax,%ax
Disassembly of section .text:
00001070 <_start>:
...
000010b0 <__x86.get_pc_thunk.bx>:
...
000010c0 <deregister_tm_clones>:
...
00001100 <register_tm_clones>:
...
00001150 <__do_global_dtors_aux>:
...
000011a0 <frame_dummy>:
11a0: 00 00 add %al,(%eax)
11a2: 00 00 add %al,(%eax)
...
000011a5 <__x86.get_pc_thunk.dx>:
11a5: 00 00 add %al,(%eax)
...
000011a9 <main>:
11a9: 00 00 add %al,(%eax)
11ab: 00 00 add %al,(%eax)
11ad: 00 00 add %al,(%eax)
...
000011b0 <__libc_csu_init>:
...
00001210 <__libc_csu_fini>:
...
Disassembly of section init:
00001211 <init_extra>:
1211: 53 push %ebx
1212: 83 ec 24 sub 0x24,%esp
1215: e8 96 fe ff ff call 10b0 <__x86.get_pc_thunk.bx>
121a: 81 c3 e6 2d 00 00 add0x2de6,%ebx
1220: 66 c7 44 24 19 31 32 movw 0x3231,0x19(%esp)
1227: c6 44 24 1b 00 movb0x0,0x1b(%esp)
122c: 8d 44 24 19 lea 0x19(%esp),%eax
1230: 50 push %eax
1231: e8 fa fd ff ff call 1030 <puts@plt>
1236: c7 04 24 00 00 00 00 movl 0x0,(%esp)
123d: e8 fe fd ff ff call 1040 <exit@plt>
Disassembly of section .fini:
00001244 <_fini>:
1244: 53 push %ebx
1245: 83 ec 08 sub0x8,%esp
1248: e8 63 fe ff ff call 10b0 <__x86.get_pc_thunk.bx>
124d: 81 c3 b3 2d 00 00 add 0x2db3,%ebx
1253: 83 c4 08 add0x8,%esp
1256: 5b pop %ebx
1257: c3 ret
有几个点需要说一下:
1、赶巧,我起节名叫init,正好把节插在了.text节的后面,这样IP能从前往后滑下来,能跑到init_extra。我后来试了下,如果真把节名起成.init,那这段代码就和最前面原本的代码合并了,那也就跑不到init_extra了。
2、赶巧,add %al,(%eax)的x86机器码恰好是00 00,而且还没报SIGSEGV,经过查vmmap,发现(%eax)恰好指向ELF Header那一节,那一节只在程序装载时有用,只要一加载完毕直接作废。所以这一节的数据都不重要,你随便改。这个节的长度是0x1000,这条指令只改ax寄存器的低4位,所以压根不用担心,随意它怎么改。
我在想(%eax)恰好指向ELF Header那一节是不是所有机器的统一标准,于是查了一下,发现人家ABI[9][10]里压根没这一说,明确有规定的只有%rsp,%rdx和%rbp,其他的都未定义。所以我估计这玩意是loader遗留下的,只要Loader在移交控制权之前把寄存器一清,这题立马SIGSEGV就做不了了。
3、不巧的是,add %al,(%eax)的x86机器码恰好是00 00,连续的两个字节都必须是00。好,结果.text节的__libc_csu_fini函数只占1个Byte,好家伙,你这直接把后面的机器码全都识别了,结果后面的全搞乱了。那么就要解决这个问题,对齐。那么解决对齐有什么办法呢?
第一个是按照官方方法里写的对齐.byte 0,当时我不知道有这么个玩意,然后又查gcc手册[6],好,发现了aligned这个attribute,这个是第二种方法。说明如下:
aligned
aligned (alignment)
The aligned attribute specifies a minimum alignment for the first instruction of the function, measured in bytes. When specified, alignment must be an integer constant power of 2. Specifying no alignment argument implies the ideal alignment for the target. The __alignof__ operator can be used to determine what that is (see Alignment). The attribute has no effect when a definition for the function is not provided in the same translation unit.
The attribute cannot be used to decrease the alignment of a function previously declared with a more restrictive alignment; only to increase it. Attempts to do otherwise are diagnosed. Some targets specify a minimum default alignment for functions that is greater than 1. On such targets, specifying a less restrictive alignment is silently ignored. Using the attribute overrides the effect of the -falign-functions (see Optimize Options) option for this function.
Note that the effectiveness of aligned attributes may be limited by inherent limitations in the system linker and/or object file format. On some systems, the linker is only able to arrange for functions to be aligned up to a certain maximum alignment. (For some linkers, the maximum supported alignment may be very very small.) See your linker documentation for further information.
The aligned attribute can also be used for variables and fields (see Variable Attributes.)
那么改完了之后,代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
__attribute__((section("init"))) __attribute__((aligned(2)))
void init_extra(){
char buf[] = "Hello, world!";
puts(buf);
exit(0);
}
int main(){}
好,那么这个时候继续跑,代码还是不行。再用gdb看,发现上面有个点没发现,继续说:
4、程序没关PIE(位置无关可执行文件),所以代码里需要用到PC相对寻址,但这个PIE是用来定位全局符号或者外部符号的,我们这个函数里压根就不需要。他前面专门调了一个__x86.get_pc_thunk.bx,把PC存到寄存器BX里了。但是这个函数它是在.text节里面的,已经被置零了。恰好我们又用不到全局符号和外部符号,所以我们怎么办呢。找个不开PIE的编译器[8]把这段代码扔进去,把他生成的汇编拿过来直接内联进去用。好,那么这样代码就变成了:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
__attribute__((section("init"))) __attribute__((aligned(2)))
void init_extra(){
// char buf[] = "Hello, world!";
// puts(buf);
// exit(0);
__asm__ __volatile__(
"subl 40, %esp\n"
"movl1819043144, 14(%esp)\n"
"movl 1998597231, 18(%esp)\n"
"movl1684828783, 22(%esp)\n"
"movw 33, 26(%esp)\n"
"leal 14(%esp), %eax\n"
"pushl %eax\n"
"call puts\n"
"movl0, (%esp)\n"
"call exit\n"
);
}
int main(){}
这样代码就能跑起来了。注意,整个实验都必须在他出题人给定的docker下进行,否则这一整套工具链哪里稍微一变,这个题就做不了了。为了方便大家研究,我把源代码还有ELF都打个压缩包传上来,供大家下载。
参考资料:
[1] https://blog.csdn.net/choumin/article/details/113938601
[2] https://code.woboq.org/userspace/glibc/csu/libc-start.c.html
[3] https://code.woboq.org/userspace/glibc/stdlib/exit.c.html
[4] https://code.woboq.org/userspace/glibc/sysdeps/unix/sysv/linux/_exit.c.html
[5] https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Function-Attributes.html
[6] https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Common-Function-Attributes.html
[7] https://www.toutiao.com/i6978232161929331214/?wid=1635602831998
[8] https://gcc.godbolt.org/
[9] https://newbedev.com/what-is-default-register-state-when-program-launches-asm-linux
[10] https://github.com/hjl-tools/x86-psABI/wiki/x86-64-psABI-1.0.pdf